Thread
This one suggests that aerobic physical activity durations of 3 hours/week and resistance training exercise ~1–2 times/week may substantively reduce the risk of all-cause mortality, with their combination confering additional mortality risk reduction beyond cardio alone.
- Higher aerobic PA duration was found to be robustly associated with lower mortality risk and was optimised at ~3 hours/week, largely independent of age and sex.
Across all models, an inverse association of aerobic PA with mortality risk with doses as short as ~1 hour/week were found, with results suggesting little additional mortality risk reduction beyond 3 hours/week.
Little difference was observed for this association when moderate aerobic PA (MPA) and vigorous aerobic PA (VPA) were examined separately.
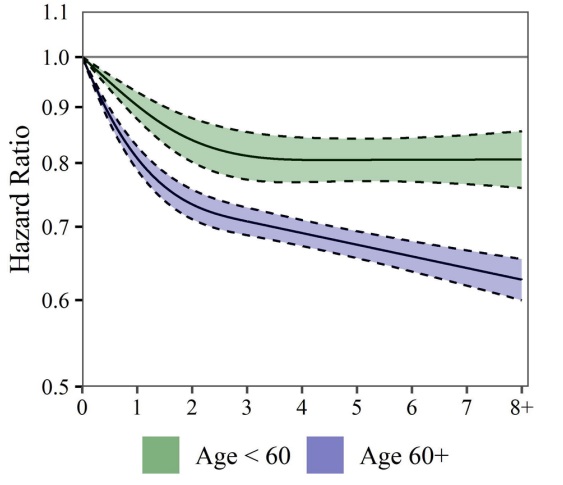
When analyses were stratified by sex and age using full cohort data, minimal differences were seen between men and women, but results suggested the inverse association between aerobic PA and mortality risk may be stronger in older individuals than younger individuals.
Additionally, there was some evidence that mortality risk reduction continues beyond 3 hours/week for older individuals.
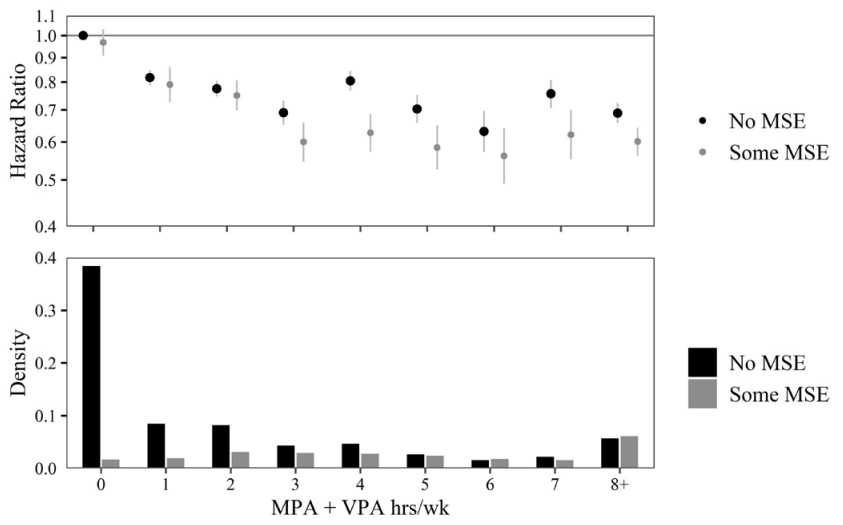
- Muscle-strengthening exercise, while having a marked inverse association with mortality risk when completed exclusively, was found to result in additional mortality risk reduction when completed in combination with aerobic PA.
An inverse association between MSE and mortality risk with as little as 1 time/week in the basic exposure model, with additional mortality risk reduction present when MSE was performed in combination with MPA and/or VPA during analyses using other exposure models.
Observations generally suggested that 1–2 times/week of MSE is likely sufficient to reduce mortality risk, with no remarkable additional benefit seen beyond this frequency.
TL;DR:
This study suggests that regardless of sex or age:
This study suggests that regardless of sex or age:
a) Significant mortality risk reduction may result from aerobic physical activity performed 1 hour/week, with minimal additional benefits beyond 3 hours/week
b) Muscle-strengthening exercise performed exclusively 1–2 times/week may result in morality risk reductions.
c) The combination of aerobic physical activity and muscle-strengthening exercise may further decrease mortality risk than each modality alone.
Dose–response association of aerobic and muscle-strengthening physical activity with mortality: a national cohort study of 416 420 US adults
dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2022-105519
#exercise #TrainHard #GymLife #GymTime #muscle #strength #lift #GetStrong #cardio #hiit
dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2022-105519
#exercise #TrainHard #GymLife #GymTime #muscle #strength #lift #GetStrong #cardio #hiit