Thread
If you run a business, you MUST understand accounting
Here is what you need to know:
Here is what you need to know:
1/ Introduction
There are a lot of MYTHS about how accounting works
At its core, accounting is based on “Accrual Accounting”
“Accrual Accounting” is a set of rules used to record business transactions
There are a lot of MYTHS about how accounting works
At its core, accounting is based on “Accrual Accounting”
“Accrual Accounting” is a set of rules used to record business transactions
In this thread I will:
1 Explain what "Accrual Accounting" is
2. Debunk common Accounting Myths
1 Explain what "Accrual Accounting" is
2. Debunk common Accounting Myths
2/ Accrual Accounting
Accrual Accounting is best understood through an example:
Let’s say you’re the owner of a store that sells pencils:
• You purchase 100 pencils for $1 each
• You then sell 50 of those pencils for $3 each
· What’s your profit?
Accrual Accounting is best understood through an example:
Let’s say you’re the owner of a store that sells pencils:
• You purchase 100 pencils for $1 each
• You then sell 50 of those pencils for $3 each
· What’s your profit?
There are a couple of ways to calculate profit:
1. Using the “Cash Method” ➡️ how most people think accounting works
2. Using the “Accrual Method” ➡️ the method accounting is based on
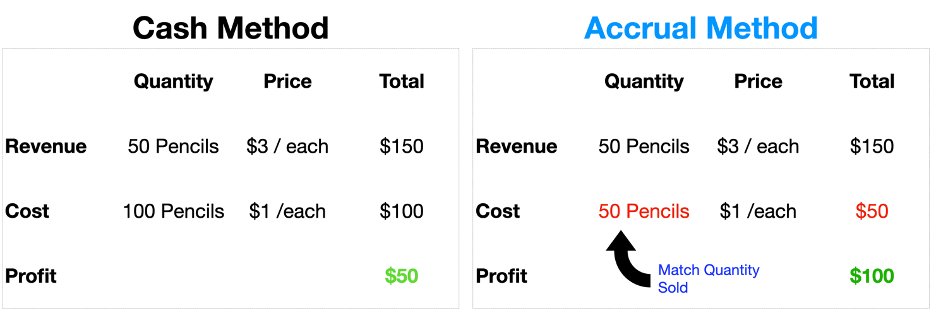
Here is a chart:
1. Using the “Cash Method” ➡️ how most people think accounting works
2. Using the “Accrual Method” ➡️ the method accounting is based on
Here is a chart:
Notice how profit is completely different under the two methods?
• It’s $50 under the CASH method
• It’s $100 under the ACCRUAL method
Why is profit different under Accrual Accounting?
• It’s $50 under the CASH method
• It’s $100 under the ACCRUAL method
Why is profit different under Accrual Accounting?
The difference in the example above lies in how “Costs” are determined
Cash Accounting:
• You bought 100 pencils for $1, so you expense everything
➡️ Cost: 100 pencils * $1 = $100
Accrual Accounting:
• You only expense 50 pencils for $1
➡️ Cost: 50 pencils * $1 = $50
Cash Accounting:
• You bought 100 pencils for $1, so you expense everything
➡️ Cost: 100 pencils * $1 = $100
Accrual Accounting:
• You only expense 50 pencils for $1
➡️ Cost: 50 pencils * $1 = $50
This is because under Accrual Accounting you have to match:
QUANTITY SOLD = QUANTITY EXPENSED
QUANTITY SOLD = QUANTITY EXPENSED
3/ Matching Principle
Generally, under accrual accounting
The QUANTITY in your COST must match the QUANTITY in your REVENUE
Why?
Because of the “Matching Principle”
Generally, under accrual accounting
The QUANTITY in your COST must match the QUANTITY in your REVENUE
Why?
Because of the “Matching Principle”
MYTH: When you purchase goods, you can expense everything right away
Accounting doesn’t work like that
Instead, you only expense the portion of the goods you SOLD
Accounting doesn’t work like that
Instead, you only expense the portion of the goods you SOLD
In the above example, that’s 50 pencils NOT 100 pencils
The remainder of the unsold pencils are capitalized and expensed ONLY when they are SOLD
The remainder of the unsold pencils are capitalized and expensed ONLY when they are SOLD
4/ Inventory
Because of the matching principle, there are consequences
One of those consequences is the creation of INVENTORY balances
Because of the matching principle, there are consequences
One of those consequences is the creation of INVENTORY balances
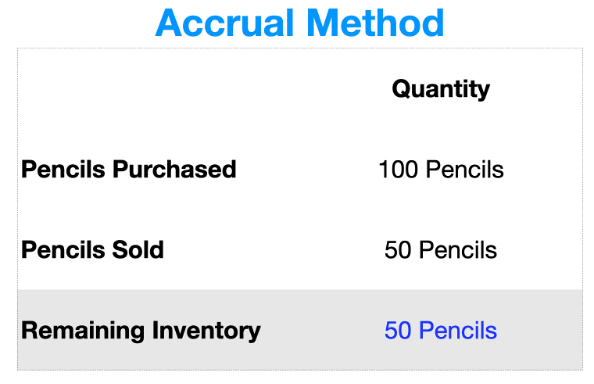
Inventory is “goods” that you’ve paid for but haven’t sold yet
These goods are capitalized on the balance sheet
In our pencils example above, the inventory balance would be calculated as:
These goods are capitalized on the balance sheet
In our pencils example above, the inventory balance would be calculated as:
5/ Capitalizing Assets
Closely related to the inventory example is the concept of Capitalizing Assets
MYTH: When a business buys a new computer, you can write-off/expense it right away
That’s not how accounting works
Closely related to the inventory example is the concept of Capitalizing Assets
MYTH: When a business buys a new computer, you can write-off/expense it right away
That’s not how accounting works
Because you will use your computer for 2 to 3 years
Accounting rules prevent you from expensing the computer when you buy it
Instead, just like inventory – the computer is capitalized and slowly expensed over time
Accounting rules prevent you from expensing the computer when you buy it
Instead, just like inventory – the computer is capitalized and slowly expensed over time
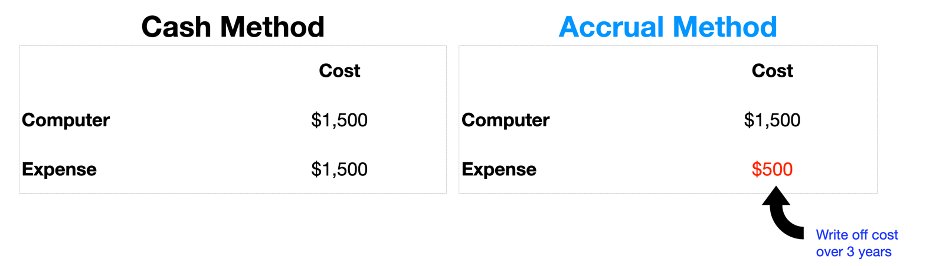
Let’s look at an example:
• You buy a computer for $1,500
• You have to expense the computer over a certain period say, 3 years
• In this case, can only expense $500 worth in the first year ($1,500 / 3 years)
• You buy a computer for $1,500
• You have to expense the computer over a certain period say, 3 years
• In this case, can only expense $500 worth in the first year ($1,500 / 3 years)
6/ Accounts Receivable
MYTH: You can only record a sale when cash is collected
Accounting doesn’t work like that
You have to record a sale when you invoice your customer
MYTH: You can only record a sale when cash is collected
Accounting doesn’t work like that
You have to record a sale when you invoice your customer
If your customer takes 1 month to pay your bill, you DON’T wait 1 month to book the sale
Instead, the sale is booked when the customer is invoiced
You then record accounts receivable to show that the customer owes you money for the sale
Instead, the sale is booked when the customer is invoiced
You then record accounts receivable to show that the customer owes you money for the sale
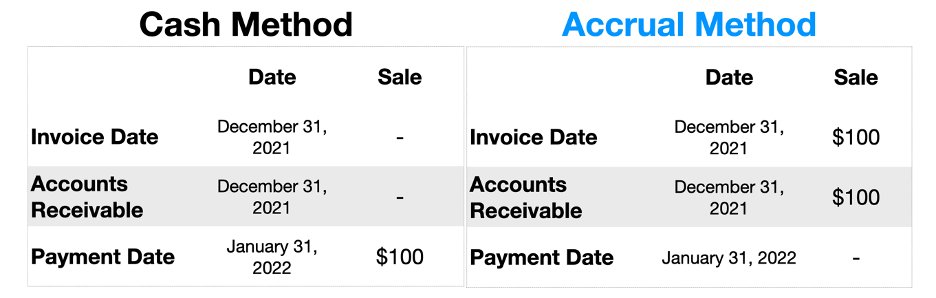
Let’s look at an example:
• You sell a service to a customer for $100
• You invoice the customer on December 31, 2021
• The customer pays on January 31, 2022
• You sell a service to a customer for $100
• You invoice the customer on December 31, 2021
• The customer pays on January 31, 2022
In the example above, For accrual Accounting:
The sale is booked in December 2021 when the customer was invoiced
NOT when payment was received
The sale is booked in December 2021 when the customer was invoiced
NOT when payment was received
7/ Accounts Payable
MYTH: You can only record an expense when you pay cash to your suppliers
Accounting doesn’t work like that
You have to record an expense when you receive a bill from a supplier
MYTH: You can only record an expense when you pay cash to your suppliers
Accounting doesn’t work like that
You have to record an expense when you receive a bill from a supplier
If you take 1 month to pay the bill, you DON’T wait 1 month to book the expense
Instead, the expense is booked when you get the bill from your supplier
You then record ACCOUNTS PAYABLE to show that you owe money to your supplier
Instead, the expense is booked when you get the bill from your supplier
You then record ACCOUNTS PAYABLE to show that you owe money to your supplier
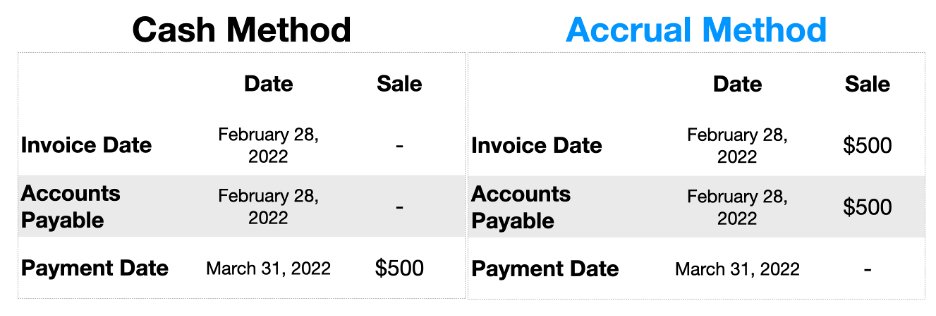
Let’s look at an example:
• You buy a service from a supplier for $500
• Your supplier sends you a bill on February 28, 2022
• You pay the bill on March 31, 2022
• You buy a service from a supplier for $500
• Your supplier sends you a bill on February 28, 2022
• You pay the bill on March 31, 2022
In the example above, for Accrual Accounting:
The expense is booked on February 28, 2022 when you RECEIVED the bill
NOT when you PAID the bill
The expense is booked on February 28, 2022 when you RECEIVED the bill
NOT when you PAID the bill
9/ Video Tutorial
Here is a short video that explains how accrual accounting works:
www.youtube.com/watch?v=OBxLJvpJ4Cc&ab_channel=THECFO
Here is a short video that explains how accrual accounting works:
www.youtube.com/watch?v=OBxLJvpJ4Cc&ab_channel=THECFO
TL;DR:
• You match revenues and expenses
• You capitalize unsold goods as inventory
• You capitalize assets
• You record revenue when a sale is made not when cash is collected
• You record expenses when you buy something not when you pay for it
• You match revenues and expenses
• You capitalize unsold goods as inventory
• You capitalize assets
• You record revenue when a sale is made not when cash is collected
• You record expenses when you buy something not when you pay for it
If you learned something new in this thread, retweet it!
Let's learn together and follow @AliTheCFO
I tweet about:
• Finance
• Business
• Personal Growth
Let's learn together and follow @AliTheCFO
I tweet about:
• Finance
• Business
• Personal Growth
Mentions
See All
Blake Burge @blakeaburge
·
Mar 21, 2022
Great thread, Ali!